A Definitive Guide to Mobile Pentesting
Think of a mobile app like a digital vault , holding everything from user passwords to payment details. As a penetration tester, your job...

The 23andMe Breach: Anatomy, Impact, and Lessons for Genomic Security (Deep Dive)
In late 2023, DNA testing company 23andMe disclosed a breach that compromised the personal and genetic data of millions of users [1] ....

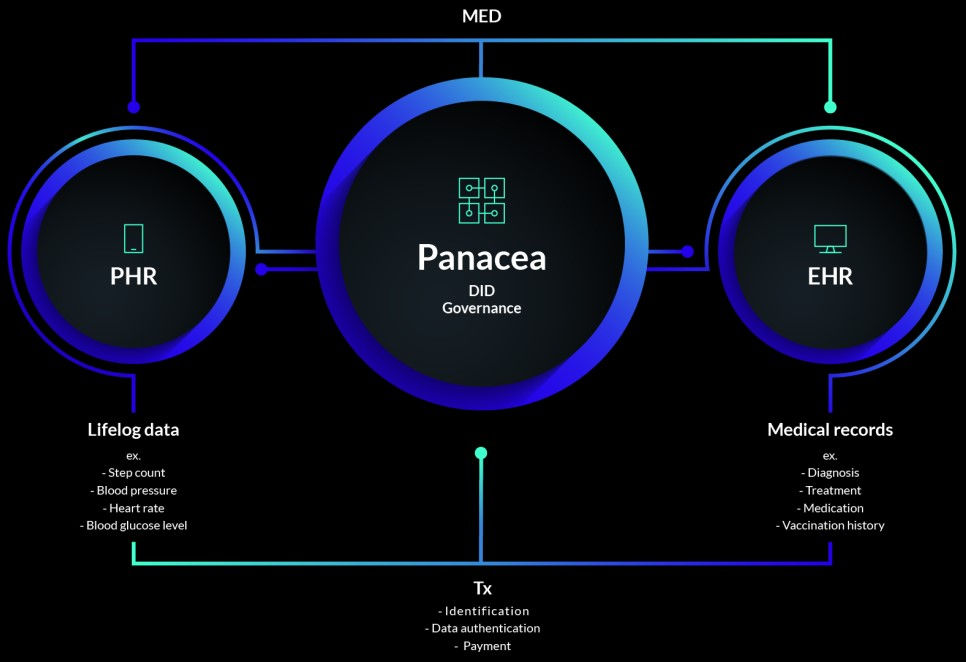
From Startup to Scale-Up: When Biotech Companies Must Take Security & Compliance Seriously
The Compliance Cliff in Medical Biotech In the fast-moving world of medical biotech, there’s a steep and often overlooked cliff:...